Improve the inspection process and gather data
Quality Control and Assurance with AI
Quality control is essential for accuracy, reliability, and optimizing production. With increasing demands, we offer three technological solutions that enhance inspection processes and data collection: assisted reality, augmented reality, and fully automated systems. These innovations minimize errors, increase efficiency, and provide valuable insights for further production optimization.

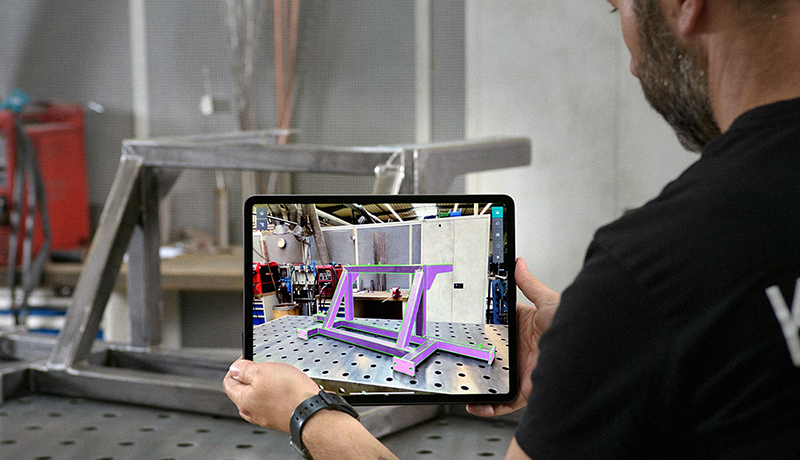
A worker with smart glasses, a tablet or a phone.
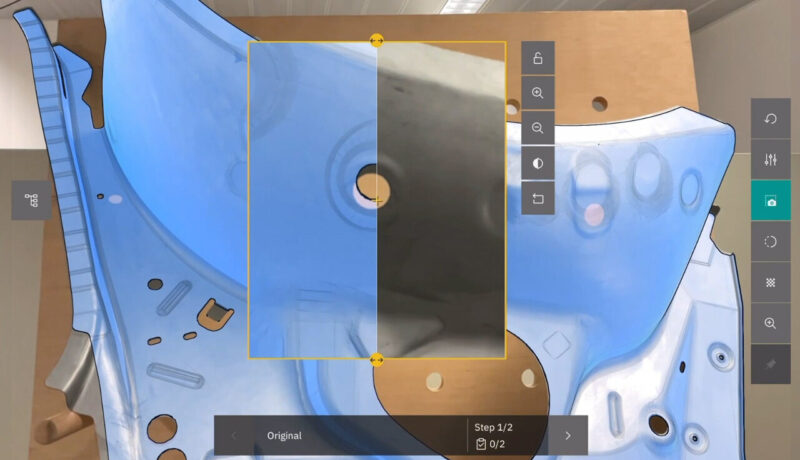
2D controls, also known as “assisted reality,” are typically process maps of screens containing text, photos, or videos, each guiding the worker step by step through the process and simultaneously collecting data while performing the task.

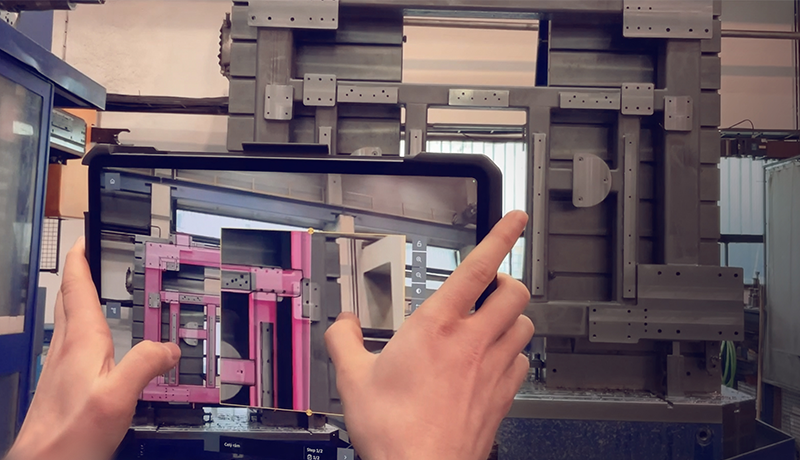
A worker with a tablet or a phone
3D controls using “augmented reality” offer a more immersive practical experience, where the 3D CAD model overlays with the actual product, allowing the inspector to directly compare the real product with the model and check for any discrepancies in real time.
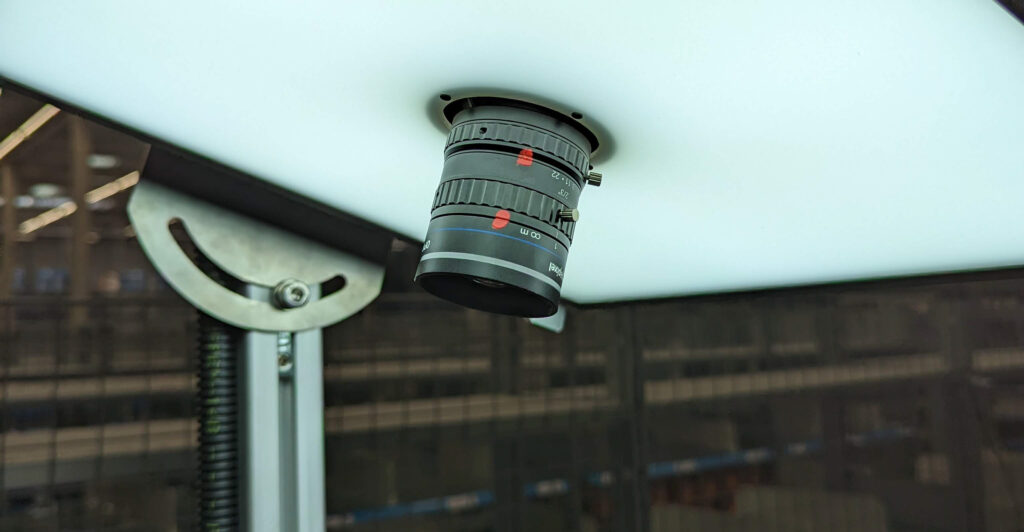

Fully automated inspection
We provide systems for the most demanding industrial applications and focus on the development and installation of complex solutions. In doing so, we leverage the power of artificial intelligence, machine vision, and neural networks.
Make quality control easier with digital technology
Quality control is key to production accuracy, safety and customer satisfaction. Modern technologies such as smart glasses, augmented reality and automation make the inspection process much easier and more efficient. By overlaying digital information onto real images, inspectors can accurately see specifications, tolerances and key inspection points right in their field of view.
Automated data collection for more accurate analysis
Systems using tablets, smart glasses or AI make it easy to collect accurate data – from numerical values to photos to videos of inspection steps. This data can be instantly processed into clear documentation or automatically sent to a database for further analysis. Digitisation thus ensures greater accuracy, speed and easier traceability of results.
The main advantages
Read more about quality control using a tablet and smart glasses.
Quality checks are crucial and an integral part of product delivery, having a significant impact on subsequent processes, safety, and customer satisfaction.
AI & Machine Vision
Types of fully automated inspection.
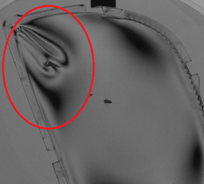
Identification of Defects and Anomalies Detecting
Detecting manufacturing defects and burrs is one of the most common issues for which machine vision is used. It can identify scratches, abrasions, fingerprints, damaged edges, production burrs, or the undesirable presence of foreign objects.

Final Inspection of Dimensions and Shapes
Reliably measure product dimensions at multiple points in a single step and compare them with the prescribed values. Parts that do not meet the parameters are marked and rejected.

Color Detection
Color detection and inspection are common tasks for machine vision. Using industrial color cameras combined with software, it is possible to check saturation, hue, and even the uniformity of a color coating.

Product Sorting
Camera systems can read and verify product quality, alert machine operators to errors, or automatically remove non-compliant products from production using simple automation

Character, Text, and QR or Bar Code Reading
Reading and verifying barcodes and matrix identification codes enable secure and continuous tracking of components and products throughout processing until delivery to the end customer.

Robot Guidance
Reducing cycle time in production through extensive data collection from multiple sensors and cameras, which are continuously analyzed and stored, leads to more efficient industrial robot operation and significant cost savings..

Production Monitoring (Traceability)
Software tools for monitoring production data and machines help evaluate weaknesses in the manufacturing process and store data over time for potential retrospective traceability.